中国激光
2022, 49(19): 1900000
1 北京航空航天大学仪器科学与光电工程学院,北京 100191
2 杭州极弱磁场重大科技基础设施研究院,浙江 杭州 310051
3 北京航空航天大学大科学装置研究院,北京 100191
无自旋交换弛豫(SERF)原子自旋惯性测量装置在前沿基础物理探索以及惯性导航领域具有广泛应用前景。建立了SERF原子自旋惯性测量装置的耦合系综动力学响应模型,通过仿真和实验量化分析了耦合系综动力学响应的影响因素,厘清了偏置磁场、耦合自旋系综极化率和弛豫率等因素对准静态响应信号的影响。发现在强耦合点与自补偿点处,动态响应速度存在75倍的显著差异。进一步分析了偏置磁场、极化率和弛豫率对不同原子组合的惯性测量装置响应系数的影响。发现在自补偿点处存在最优极化率,使惯性测量装置的角速度响应系数最高,此最优点与原子种类和电子自旋弛豫率相关,可以通过降低电子自旋弛豫率将角速度响应系数提升近1倍。明确了通过优化电子自旋极化率和抑制电子自旋弛豫率可以进一步提升SERF原子自旋惯性测量灵敏度和动态性能,有望拓展其在惯性导航和基础物理探索中的应用。
中国激光
2022, 49(19): 1904001
北京航空航天大学仪器科学与光电工程学院, 北京 100191
采用基于圆偏振探测光的光纤Sagnac原子自旋进动闭环检测技术,实验测试了无自旋交换弛豫(SERF)原子自旋陀螺在两种不同抽运状态下的角速度输入/输出特性,发现了SERF原子自旋陀螺输出的非线性现象。基于SERF原子自旋陀螺理论,建立了非线性响应模型并进行仿真研究,仿真结果与实验测试一致。研究表明:SERF原子自旋陀螺的非线性由原子内在相互作用决定,与总电子弛豫率Rtot密切相关。
光纤光学 陀螺仪 无自旋交换弛豫 原子自旋陀螺 圆偏光 非线性响应 电子弛豫率
北京航空航天大学仪器科学与光电工程学院, 北京 100191
分析了极化碱金属气室的旋光特性,极化的原子气室宏观上可等效为一种法拉第旋光晶体,其旋光系数与原子自旋进动相关。提出了采用圆偏振探测光测量通过气室的左右旋圆偏振光相位差来实现原子自旋进动检测的思路。基于改进的全光纤反射型Sagnac干涉仪,搭建了光纤原子自旋进动检测系统,通过圆偏振探测光实现了无自旋交换弛豫态自旋进动信号的检测。在原子自旋陀螺仪实验平台上进行了实验验证并实现了陀螺效应,实验结果证明了所提理论的正确性。对陀螺性能进行了初步测试,得到其零偏不稳定性为0.29 (°)/h。
测量 光纤光学 相干检测 原子自旋进动检测 Sagnac干涉仪 无自旋交换弛豫 圆偏振光
Author Affiliations
Abstract
School of Instrumentation Science and Opto-electronics Engineering, Beihang University, Beijing 100191, China
A superluminescent diode (SLD) as an alternative of laser is used to detect optical rotation for atomic spin precession. A more uniform Gauss configuration without additional beam shaping and a relatively high power of the SLD have a potential for atomic magnetometers, which is demonstrated in theory and experiments. In addition, the robustness and compactness enable a more practical way for optical rotation detections, especially for applications in magnetoencephalography systems.
Superluminescent diode atomic magnetometer magnetoencephalography atomic spin precession detection Larmor precession Photonic Sensors
2019, 9(2): 02135
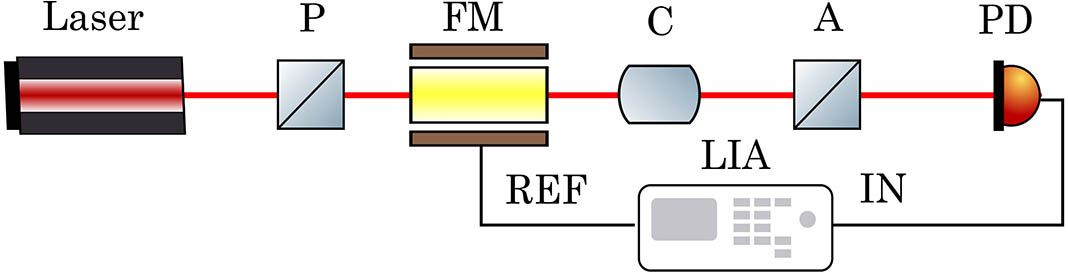
Author Affiliations
Abstract
School of Instrumentation Science & Opto-Electronics Engineering, Beihang University, Beijing 100191, China
The measurement of an extremely small magneto-optical polarization rotation angle with high sensitivity is integral to many scientific and technological applications. In this Letter, we have presented a technique based on Faraday modulation combined with the optical differential method to measure an extremely small polarization rotation angle with high sensitivity. The theoretical and experimental results show that common mode noise is reduced appreciably and signal to noise ratio is enhanced. The effectiveness of this technique has been demonstrated by measuring the Verdet constant of terbium gallium garnet glass and measuring the small polarization rotation angle. A sensitivity of enhancement of one order of magnitude has been achieved using differential detection based on Faraday modulation.
120.5410 Polarimetry 000.3110 Instruments, apparatus, and components common to the sciences 040.1880 Detection Chinese Optics Letters
2018, 16(8): 081201
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 School of Instrumentation Science and Opto-Electronics Engineering, Beihang University, Beijing 100191, China
2 Key Laboratory on Inertial Technology, Beijing 100191, China
In this Letter, the liquid crystal variable phase retarder is applied for the accurate modulation of the laser power in a detection system and the construction of a system that suppresses the influence of laser noise on the gyro’s bias instability. A closed-loop control method for a laser noise suppression system is proposed. We obtain a power stability index of 0.038% in a 3-h continuous test, and the nuclear magnetic resonance gyroscope bias instability reaches 1°/h. The proposed control method effectively improves the signal-to-noise ratio of the gyroscope detection signal, which lays the technical foundation for future research work.
230.0230 Optical devices Chinese Optics Letters
2017, 15(8): 082302
北京航空航天大学 仪器科学与光电工程学院,北京 100191
基于折射率界面厚度的描述建立了一种高折射率梯度门限的数学模型,在此梯度门限下,研究了高超声速流场中高折射率梯度区域的气动光学传输效应。提出了一种用折射率梯度的调和平均值描述高折射率梯度门限的方法。采用高超声速流场的计算流体力学结果作为分析折射率梯度和进行气动光学传输仿真的源数据,忽略绝对值低于该门限的梯度值重构折射率场,并采用变折射率介质中光线追迹算法仿真其气动光学传输畸变。不同流场状况、不同位置截面的仿真结果表明,采用本门限,重构折射率场和原折射率场的相关性达0.9以上,仿真光程差均方根的相对误差不超过±5%,验证了该高折射率梯度门限模型的有效性和适用性,同时从数值角度证实了高超声速湍流流场中高折射率梯度区域是气动光学传输畸变的主要成因。
大气光学 湍流 光学传输[折射率梯度





